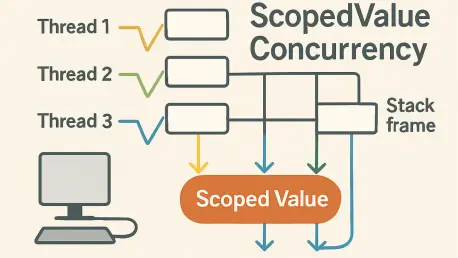
Imagine a bustling server environment where millions of virtual threads handle simultaneous requests, each needing specific context data to function correctly, yet the risk of memory leaks and data corruption looms large. This scenario underscores a persistent challenge in Java concurrent programming: managing context efficiently and safely across threads. Enter ScopedValue, a transformative feature introduced in Java, designed to tackle these very issues with a fresh approach to context management. This review dives deep into the capabilities of ScopedValue, evaluating its innovative design, performance benefits, and real-world applicability in modern multi-threaded applications. By exploring its strengths and limitations, this analysis aims to shed light on how this feature is reshaping concurrency in Java.
Evolution of Context Management in Java
Struggles with Traditional Approaches
Managing context in early Java applications often relied on rudimentary techniques like passing data through method parameters. While straightforward, this method quickly becomes cumbersome in complex systems, cluttering code with unnecessary arguments passed down through layers of calls. Such an approach not only obscures the intent of functions but also poses risks when mutable data is altered unexpectedly along the chain, complicating debugging efforts.
Another common tactic involved using global variables or singleton patterns to share context across threads. However, this introduced significant performance bottlenecks due to the need for synchronization, as multiple threads accessing shared data led to contention. Moreover, maintaining thread-specific states with mutable global context proved impractical, often resulting in unpredictable behavior in concurrent settings.
Pitfalls of ThreadLocal Variables
For years, ThreadLocal variables served as a go-to solution for thread-specific data storage, eliminating the need for explicit parameter passing. Despite their utility, these variables come with notable drawbacks, including unconstrained mutability that allows any method to alter values, risking data integrity. Additionally, their unbounded lifetime means values persist unless manually cleared, frequently leading to memory leaks in thread pools.
Perhaps most critically, ThreadLocal struggles in environments with virtual threads due to costly inheritance mechanisms. When child threads inherit all parent thread data, memory overhead skyrockets, especially with the massive concurrency enabled by virtual threads. This inefficiency highlights the urgent need for a more scalable context management solution in modern Java.
Core Innovations of ScopedValue
Ensuring Data Integrity through Immutability
At the heart of ScopedValue lies its commitment to immutability, a design choice that prevents context corruption by prohibiting changes to bound values within a scope. This ensures a consistent data flow across threads, offering developers greater confidence in the reliability of shared information. As a result, debugging becomes less of a burden, with fewer unexpected state changes to track down.
This focus on immutable context also aligns with best practices in concurrent programming, where predictable behavior is paramount. By restricting modifications, ScopedValue fosters a disciplined approach to data sharing, making it particularly valuable in high-stakes applications where data consistency cannot be compromised.
Streamlined Resource Management with Bounded Lifetime
Unlike its predecessor, ScopedValue introduces a bounded lifetime for context data, automatically cleaning up when a defined scope concludes. This eliminates the memory leak risks associated with lingering values in ThreadLocal, a persistent issue in long-running thread pools. Such automatic resource management simplifies maintenance, especially in dynamic environments.
This feature proves especially beneficial when dealing with virtual threads, which are often short-lived yet numerous. The ability to discard context data effortlessly at the end of a scope reduces overhead, ensuring systems remain lean and responsive even under heavy concurrent workloads.
Clarity and Control via Dynamic Scoping
Dynamic scoping in ScopedValue restricts context access to a specific execution scope, meaning data is only available to the caller and its callees during that period. This strict boundary enhances code clarity by making data flow explicit and predictable, reducing the likelihood of misuse or unauthorized access.
Furthermore, enforcing such access control contributes to security by preventing unintended parts of an application from interacting with sensitive context. Developers benefit from a more structured codebase, where the scope of data is as apparent as the logic itself, paving the way for more maintainable and robust software design.
Alignment with Modern Concurrency Trends
The rise of virtual threads and structured concurrency in Java has created a pressing demand for context management solutions that can keep pace with lightweight, scalable models. ScopedValue meets this need by offering a mechanism tailored to handle the sheer volume of threads without the memory burden of traditional approaches. Its design minimizes overhead, making it a natural fit for these advancements.
Integration with tools like StructuredTaskScope further amplifies its relevance, as it supports disciplined thread hierarchies and context inheritance without costly data duplication. This synergy reflects Java’s broader push toward efficient concurrency frameworks that prioritize both performance and developer experience in large-scale systems.
Practical Applications in Real-World Scenarios
In practice, ScopedValue shines in scenarios requiring immutable context propagation, such as request handling in web servers where each request must carry specific metadata. Other use cases include detecting re-entrant code to prevent recursive errors, managing nested transactions in database operations, and sharing framework-specific context across components without risk of alteration.
Industries like financial technology and e-commerce, where data integrity and scalability are non-negotiable, stand to gain significantly from this feature. By ensuring safe and efficient context sharing, ScopedValue enables these sectors to build resilient applications capable of handling high transaction volumes with minimal friction.
Navigating Challenges and Constraints
Despite its strengths, ScopedValue is not a universal solution and has limitations that developers must consider. It is ill-suited for mutable data or unstructured sharing between unrelated threads, areas where ThreadLocal may still hold an edge. This constraint necessitates a clear understanding of application needs before adoption.
Migration from existing ThreadLocal implementations also poses challenges, as not all use cases align with the immutable, scoped nature of this feature. Careful evaluation is required to avoid performance pitfalls or design mismatches, ensuring that the transition enhances rather than hinders system behavior.
Looking Ahead at Potential Enhancements
As Java concurrency continues to evolve, ScopedValue holds promise for further optimization, particularly in performance tuning and deeper integration with emerging tools. Enhancements over the coming years, from now to 2027, could focus on refining cache mechanisms and expanding compatibility with diverse threading models, broadening its applicability.
Its long-term impact may lie in shaping safer multi-threaded development practices, encouraging a shift toward immutable and structured data handling. If these trajectories hold, ScopedValue could become a cornerstone of concurrent programming, influencing how developers approach context in increasingly complex applications.
Final Reflections on ScopedValue’s Contribution
Reflecting on this evaluation, it becomes clear that ScopedValue marks a significant leap forward in addressing Java’s long-standing context management woes. Its emphasis on immutability, bounded lifetime, and dynamic scoping delivers tangible improvements in safety and efficiency. For developers grappling with concurrency challenges, the next step involves assessing specific project requirements to determine if this feature aligns with their needs. Exploring pilot implementations in controlled environments offers a practical way to gauge its benefits firsthand. As the Java ecosystem continues to advance, staying attuned to updates and community insights around ScopedValue promises to unlock even greater potential in building robust, scalable systems.